Corpus of Linguistic Acceptability
View DatasetCoLA is a linguistic acceptability task where the goal is to predict whether an English sentence is grammatically acceptable.
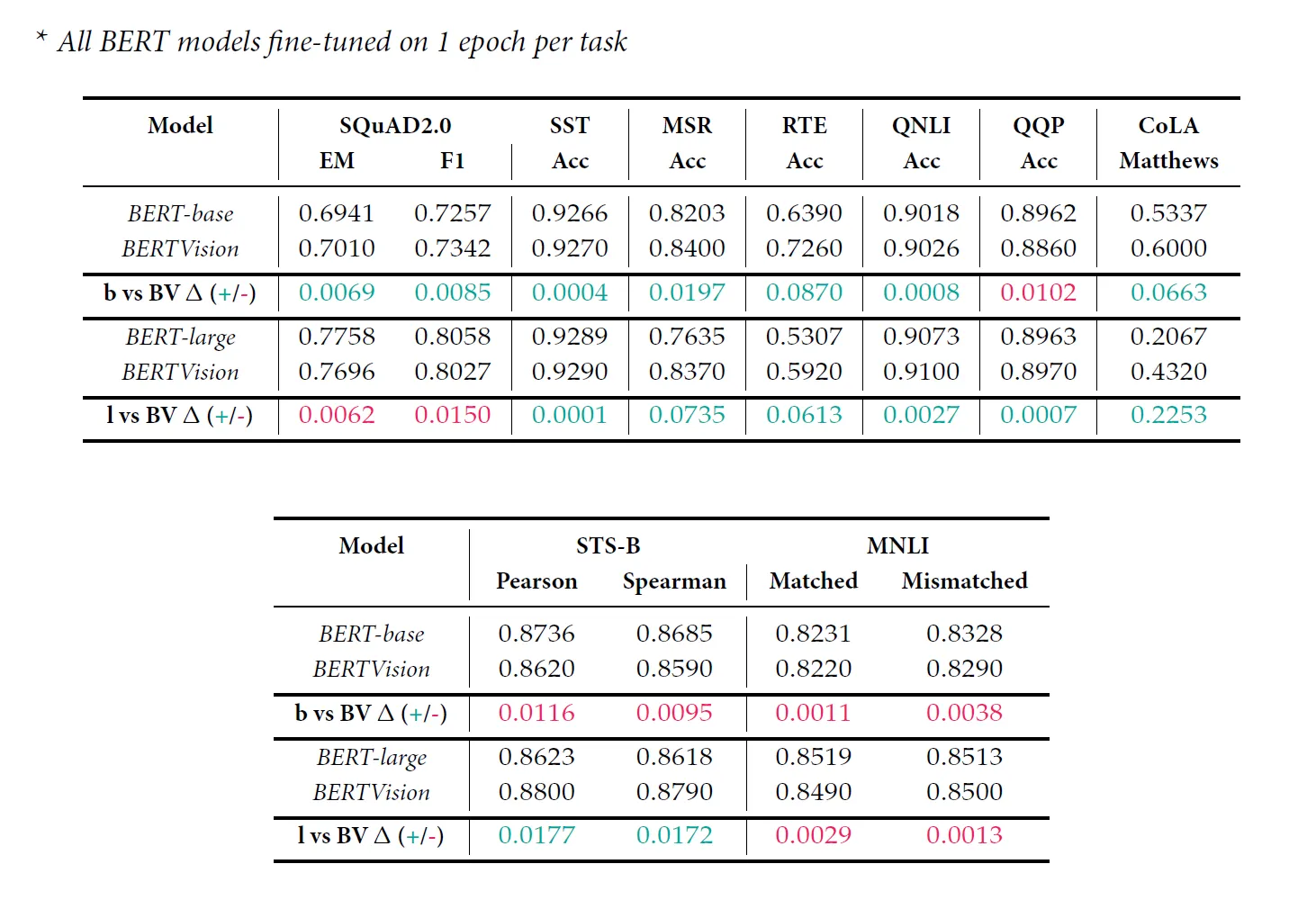
| Matthews | 53.37% | 20.67% | 60.00% | 43.20% |
Run the following commands from BERTVision/code/torch to
replicate these results:
python -m models.bert_glue --model CoLA --checkpoint bert-base-uncased --lr 9.6296e-6 --num-labels 2 --max-seq-length 128 --batch-size 16 --seed 441
python -m models.ap_glue --model AP_CoLA --checkpoint bert-base-uncased --lr 2.25972e-5 --num-labels 2 --max-seq-length 128 --batch-size 16 --seed 563
python -m models.bert_glue --model CoLA --checkpoint bert-large-uncased --lr 9.4471e-6 --num-labels 2 --max-seq-length 128 --batch-size 16 --seed 203
python -m models.ap_glue --model AP_CoLA --checkpoint bert-large-uncased --lr 2.99619e-5 --num-labels 2 --max-seq-length 128 --batch-size 16 --seed 949